Differences Between Single-Mode Fiber and Multimode Fiber Optic Cables
Introduction to Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables have revolutionized the way data is transmitted, offering unparalleled speed and reliability. The evolution of fiber optic technology has been remarkable, with continuous advancements leading to higher bandwidth and faster transmission rates. From the early days of glass fibers to the current state-of-the-art optical communication systems, the journey of fiber optics has been nothing short of extraordinary.
In today's digital world, where seamless connectivity and high-speed data transfer are paramount, fiber optic cables play a pivotal role. Their ability to transmit large volumes of data over long distances with minimal signal loss makes them indispensable in various industries, including telecommunications, internet services, and networking.
The importance of fiber optic cables in modern communication networks cannot be overstated. They form the backbone of global internet infrastructure, enabling high-speed data transfer across continents and facilitating real-time communication on a massive scale. As technology continues to advance, the demand for fiber optic cables will only continue to grow, driving further innovation in this critical field.
In the next section, we will delve into the core differences between single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables and their respective applications in different real-world scenarios.
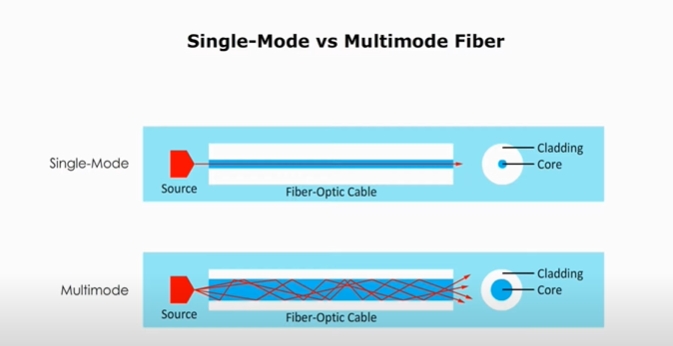
Core Diameter and Light Propagation
When it comes to single-mode fiber and multimode fiber, one of the key distinguishing factors lies in their core diameters and how light propagates through them.
Single-mode Fiber
Single-mode fiber is characterized by its extremely narrow core, typically around 8-10 microns in diameter. This slender core allows only a single mode of light to propagate through the fiber, resulting in significantly less dispersion compared to multimode fibers. The light source used for single-mode fiber is usually a laser diode, emitting a focused beam of light that stays confined within the tiny core.
Multimode Fiber
In contrast, multimode fiber features a larger core diameter, typically ranging from 50 to 100 microns. This wider core enables multiple modes of light to travel through the fiber simultaneously, leading to modal dispersion over longer distances. The light source for multimode fiber is often an LED (Light Emitting Diode), producing a broader beam of light that can traverse the larger core more easily.
The differences in core diameter and light propagation have significant implications for the performance and applications of these two types of optical fibers. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the most suitable fiber optic solution based on specific transmission requirements.
Applications in the Real World
Single-mode fiber
Single-mode fiber optic cables are widely utilized in telecommunications and internet service infrastructures. Their ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss makes them indispensable for intercontinental communication networks. The narrow core diameter of single-mode fibers allows for the transmission of a single mode of light, enabling high bandwidth and low dispersion over extended distances.
In the realm of telecommunications, single-mode fiber plays a crucial role in enabling seamless global connectivity. It forms the backbone of international communication networks, facilitating the transfer of vast amounts of data across continents. Whether it's transmitting phone calls, video conferences, or internet traffic, single-mode fiber ensures that information travels swiftly and reliably across the world.
Moreover, in the context of internet services, single-mode fiber is instrumental in supporting high-speed data transfer. It enables the seamless flow of digital information across vast geographical areas, ensuring that users can access online content and services without experiencing significant delays or disruptions.
The unparalleled performance of single-mode fiber makes it an ideal choice for applications where long-distance data transmission is paramount. Its widespread use in undersea communication cables and long-haul network connections underscores its critical role in maintaining global connectivity.
Multimode fiber
On the other hand, multimode fiber finds extensive applications in local area networks (LANs) and data centers. With its larger core diameter, multimode fibers are well-suited for transmitting data over relatively shorter distances within confined spaces.
In local area networks, multimode fiber facilitates high-speed data transfer within office buildings, campuses, or other localized environments. It supports the seamless exchange of information between interconnected devices, contributing to efficient internal communication systems within organizations.
Furthermore, multimode fiber is commonly deployed within data centers to interconnect servers, storage systems, and networking equipment. Its ability to transmit multiple modes of light over short distances makes it an ideal solution for facilitating rapid data exchange within these centralized computing facilities.
The versatility of multimode fiber makes it an essential component in creating interconnected systems that enable efficient data sharing and resource utilization within localized environments.
The Role of Hybrid Fiber Adapters
Bridging the Gap Between Single-mode and Multimode
Hybrid fiber adapters play a crucial role in seamlessly integrating single-mode and multimode fiber optic cables within a unified network infrastructure. By providing the necessary interfaces to connect different types of fibers, hybrid adapters enable the transmission of data across varying distances and environments without compromising on performance.
These adapters serve as essential components in scenarios where the existing network infrastructure comprises a mix of single-mode and multimode fibers. They facilitate smooth transitions between different fiber types, ensuring that data can flow uninterrupted across diverse optical networks. This capability is particularly valuable in situations where upgrades or expansions necessitate the coexistence of multiple fiber types.
The versatility of hybrid fiber adapters extends to their practical applications in diverse settings, including enterprise networks, telecommunications systems, and industrial environments. Their ability to bridge the gap between disparate fiber optic technologies makes them indispensable for maintaining seamless connectivity and data transfer capabilities across complex infrastructures.
However, it's important to note that while hybrid fiber adapters offer significant advantages in interoperability, they may introduce minimal signal loss or insertion loss due to the transition between different fiber types. Careful consideration of these limitations is essential when deploying hybrid adapters to ensure optimal performance within the network architecture.
Practical Applications and Limitations
In practical terms, hybrid fiber adapters are commonly employed in scenarios where the integration of single-mode and multimode fibers is necessary. Their use is prevalent in environments such as large-scale data centers, where diverse optical connections are required to support various networking equipment and storage systems.
Moreover, industrial settings often leverage hybrid fiber adapters to accommodate the coexistence of different generations of optical communication technologies. This enables seamless upgrades while maintaining compatibility with existing infrastructure, thereby optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing disruptions during transitions.
While hybrid fiber adapters offer invaluable flexibility in integrating distinct fiber optic cables, it's essential to consider their inherent limitations. The transition between single-mode and multimode fibers may introduce minimal signal loss or insertion loss, which can impact overall network performance if not carefully managed.
See Also
Contrasting LC and Duplex LC Connectors for Fiber Optic Comms
Comparing LC/UPC and SC/UPC Connectors for Multimode Fiber Patch Cables
Fiber Optic Cables Providing Single Mode Transmission
Contrasts Between MTP and LC/UPC Optical Cables for 100G Cabling


