Understanding the 2.0mm SC/UPC to SC/UPC 62.5/125um Multimode Duplex Fiber Optical Patch Cable
Dive Into the World of Fiber Optical Technology
Fiber optic technology has revolutionized the way we transmit data and communicate, making it an integral part of our modern world. Fiber Optical cables are designed to transmit data using light signals, offering several advantages over traditional copper wiring systems.
What Makes Fiber Optical So Special?
A Brief History of Fiber Optical
The concept of transmitting light through fibers dates back to ancient times, but it wasn't until the 1960s that practical optical fibers were developed for telecommunications. Over the years, advancements in technology have led to the widespread use of fiber optics in various industries.
The Basics of How It Works
At its core, fiber optic technology relies on the principle of total internal reflection. This means that light signals bounce off the walls of the fiber cables, allowing them to travel long distances with minimal loss in signal strength.
The Role of Fiber Optical in Our Daily Lives
Internet and Communication
In today's digital age, Fiber Optical technology forms the backbone of high-speed internet connections and telecommunications networks. It enables rapid data transmission and supports the increasing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications.
Medical and Research Fields
Beyond communication, fiber optics plays a crucial role in medical imaging devices and scientific research equipment. Its ability to transmit high-quality images and data with minimal interference has transformed medical diagnostics and scientific discoveries.
The Heart of Our Topic: Multimode Duplex SC/UPC Patch Cable
Now, let's delve into the intricate details of the Multimode Duplex SC/UPC Patch Cable and understand the significance of each component.
Breaking Down the Name: What Does It All Mean?
Understanding "Multimode"
When we refer to Multimode in the context of fiber optics, we are highlighting the capability of the cable to carry multiple light rays simultaneously. This is achieved through a larger core diameter, allowing various light modes to propagate through the optical fibers.
The Significance of "Duplex"
The term Duplex indicates that the cable consists of two separate transmission paths. In practical terms, this means that data can be transmitted in both directions simultaneously, enabling efficient and bidirectional communication.
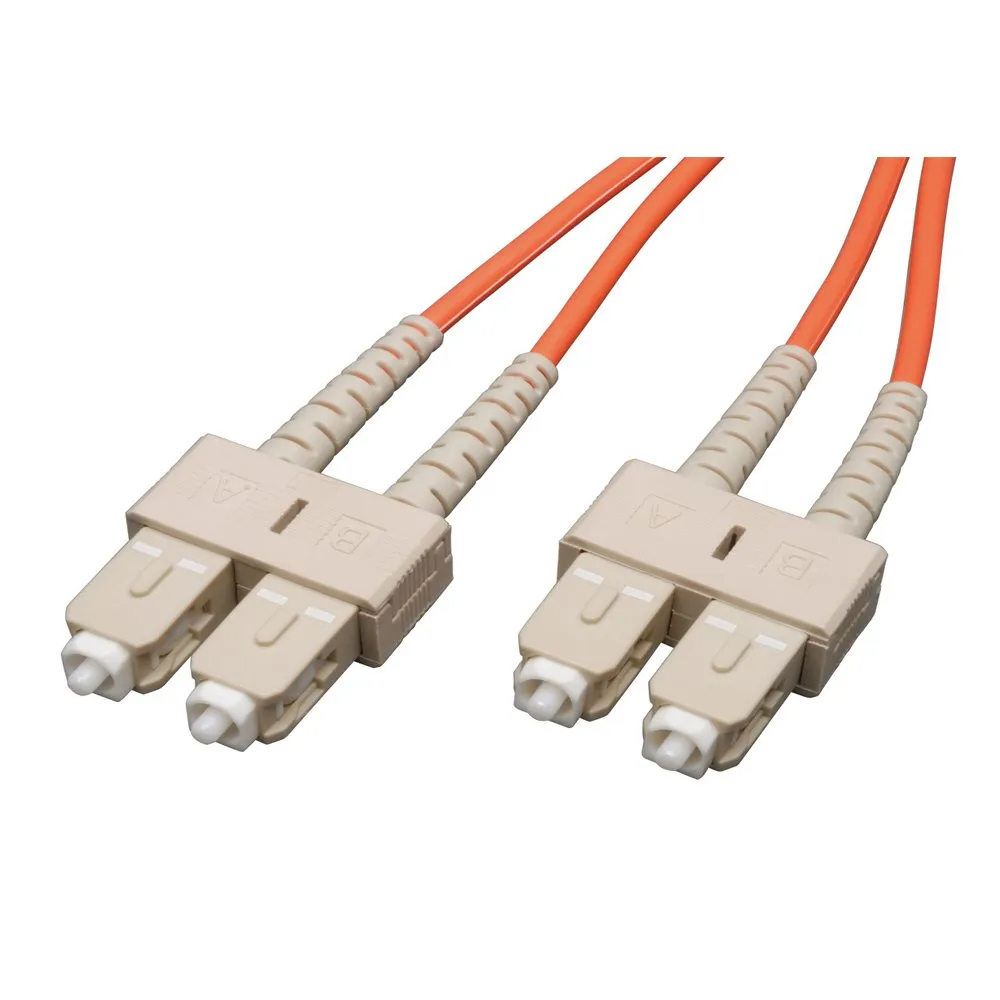
The SC/UPC Connector: A Closer Look
Design and Functionality
The SC/UPC connector is a type of fiber optic connector known for its square-shaped design and push-pull coupling mechanism. Its structure ensures precise alignment and low insertion loss, making it suitable for high-speed data transmission applications.
Why SC/UPC Stands Out
The SC/UPC connector stands out due to its ease of use and reliable performance. Its push-pull coupling mechanism allows for quick and secure connections, while the UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) polish enhances signal quality by minimizing back reflection.
Why the Specifics Matter: Understanding 62.5/125um
When it comes to fiber optic cables, the numbers associated with them hold significant importance. 62.5/125um refers to the diameters of the core and cladding of the fiber, playing a crucial role in determining its performance and applications.
Decoding the Numbers: 62.5/125um Explained
The Importance of Diameter in Fiber Optics
The 62.5/125um measurement represents the core diameter and cladding diameter of the fiber optic cable. The larger core allows for multiple modes of light to propagate simultaneously, making it suitable for short-distance data transmission within buildings and campuses.
How These Measurements Affect Performance
The specific measurements of 62.5/125um impact the cable's ability to carry light signals effectively over varying distances. While it may not support long-distance transmissions as efficiently as smaller core cables, it excels in providing cost-effective solutions for high-speed data and voice applications within limited geographic areas.
Practical Applications and Benefits
High-Speed Data and Voice Applications
The 62.5/125um Multimode Duplex SC/UPC Patch Cable is well-suited for high-speed data transfer within local area networks (LANs) and telecommunications systems. Its design allows for efficient transmission of large volumes of data, making it ideal for supporting bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming, cloud computing, and VoIP services.
The Advantages of Using This Specific Cable
Employing a Multimode Duplex SC/UPC Patch Cable with a 62.5/125um configuration offers several advantages. It provides reliable connectivity for network infrastructure, ensuring seamless communication between devices while maintaining cost-effectiveness in shorter-range deployments.
Wrapping It Up
Recap of Key Points
As we conclude our exploration of the Multimode Duplex SC/UPC Patch Cable and the world of Fiber Optical technology, let's recap the key points that we've covered. We've delved into the history and functionality of fiber optics, understanding its pivotal role in modern communication and technological advancements. Additionally, we've dissected the specifics of the 62.5/125um fiber optic cable, highlighting its practical applications and benefits in high-speed data transmission.
The Future of Fiber Optical Technology
Emerging Trends
Looking ahead, the future of Fiber Optical technology holds exciting prospects. With ongoing advancements in optical networking and data transmission technologies, we can anticipate even faster and more reliable communication systems. Moreover, innovations in fiber optic materials and manufacturing processes are likely to enhance the efficiency and affordability of these technologies.
My Final Thoughts and Encouragement
In conclusion, exploring the intricacies of Fiber Optical technology offers a glimpse into the remarkable progress that has shaped our modern world. As we continue to embrace these advancements, I encourage you to stay curious about emerging technologies and their impact on our daily lives. The journey of discovery in this field is boundless, with endless opportunities for learning and innovation.
See Also
Choosing the Perfect Duplex Multimode Fiber Optical Patch Cable
Mastering the SC UPC Single-Mode Field Assembly Optical Connector
Spotting Variances in LC/UPC and SC/UPC Connectors for Fiber Cables
Overcoming Fiber Interconnection Hurdles with SC UPC Connectors
Picking the Perfect Custom Duplex OM1 Multimode Fiber Patch Cable


